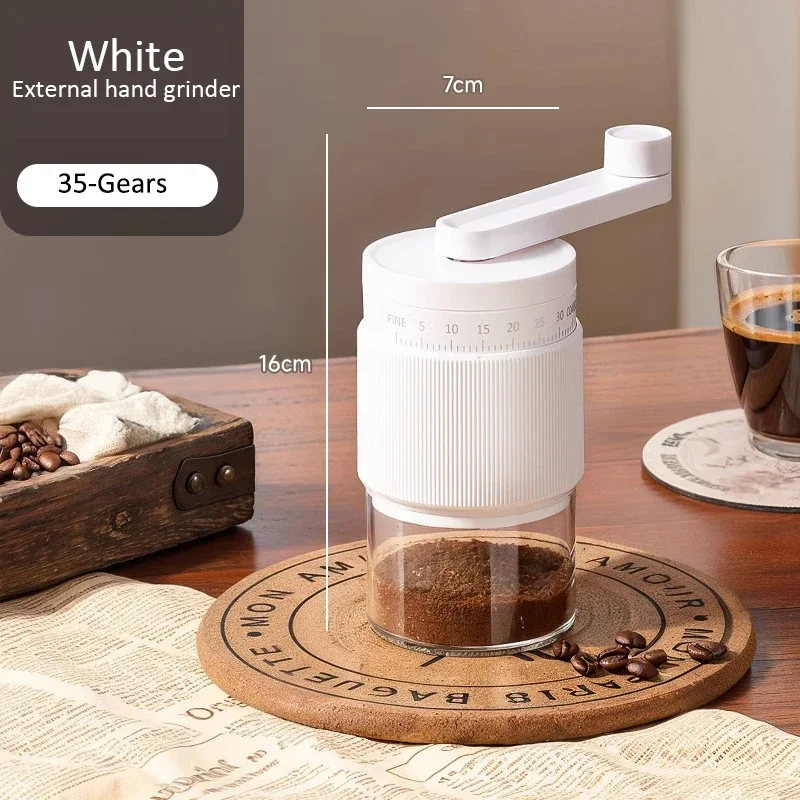
Introduction: Understanding the Dual Nature of Burrs
When people search for information about “burrs,” they’re typically referring to one of two completely different things: the grinding mechanism in coffee grinders or the unwanted rough edges left after manufacturing metal parts. The material used in either case significantly impacts performance and results.
In coffee grinding, burrs are the heart of quality grinders. They crush beans between two surfaces to create consistent grounds essential for proper extraction. The material these burrs are made from directly affects:
– Grind consistency
– Heat generation during grinding
– Durability and lifespan
– Flavor in your final cup
In manufacturing, burrs refer to those sharp, unwanted edges that form during machining processes. Removing these burrs (deburring) requires tools made from materials specifically suited to the task.
This guide explores both worlds—first examining the materials used in coffee grinder burrs, then covering the materials used for deburring tools. Understanding the ceramic vs steel burr coffee grinders options will establish a foundation for the detailed comparisons to follow.
The Science Behind Coffee Grinder Burrs
Coffee extraction is fundamentally a scientific process. When hot water passes through ground coffee, it dissolves and extracts various compounds at different rates. The size and consistency of coffee particles directly determine which flavors end up in your cup.
This is where burr material becomes crucial. Different materials create different grinding characteristics:
- Surface texture affects how beans fracture
- Material hardness determines how consistently particles are sized
- Heat conductivity influences whether the grounds maintain their aromatic compounds
The physical properties of burr materials determine how well they maintain their sharp edges through repeated use. This edge retention directly affects grind consistency over time.
Understanding how coffee flavor relates to ceramic versus steel burrs helps explain why certain materials are preferred for specific brewing methods. For example, materials that generate less heat may preserve more delicate flavor compounds sought after in pour-over brewing.
Steel Burrs: The Industry Standard
Steel burrs represent the most common material choice in quality coffee grinders, with good reason. These burrs come in several varieties, each with specific characteristics.
Stainless Steel Burrs
- Advantages:
- Excellent durability and strength
- Sharp cutting edges that maintain consistency
- Less prone to cracking if foreign objects enter the grinder
- Typically more affordable than premium alternatives
Better for coarser grounds (French press, drip coffee)
Disadvantages:
- Conduct more heat during grinding
- May wear faster than some alternatives
- Can potentially affect coffee flavor during long grinding sessions
Hardened Steel Burrs
These premium options undergo additional treatments to enhance their properties:
– Increased hardness for better edge retention
– More consistent particle size distribution
– Extended lifespan compared to standard stainless steel
The heat retention differences between steel and ceramic burrs are particularly important for espresso enthusiasts, where slight temperature changes can affect extraction. For commercial settings, steel burrs excel in high-volume operations due to their resistance to damage and consistent performance under heavy use.
Ceramic Burrs: Precision and Durability
Ceramic burrs offer distinct advantages that make them popular for certain applications. Made primarily from zirconium oxide, these burrs are extremely hard—often harder than steel counterparts.
Benefits of Ceramic Burrs:
- Exceptional hardness (8-8.5 on the Mohs scale compared to steel at 5-6)
- Significantly less heat generation during grinding
- Longer edge retention and overall lifespan
- Non-corrosive properties
- Particularly excellent for fine, consistent grinds needed for espresso
Limitations to Consider:
- More brittle than steel—can crack if stones or other hard objects enter the grinder
- Usually more expensive than standard steel burrs
- May not perform as well for very coarse grinds
The ceramic vs steel burr comparison reveals that ceramic options often provide better temperature stability during grinding, which many coffee enthusiasts believe helps preserve volatile aromatic compounds. Our ceramic burr coffee grinder collection includes models specifically designed to maximize this material’s advantages.
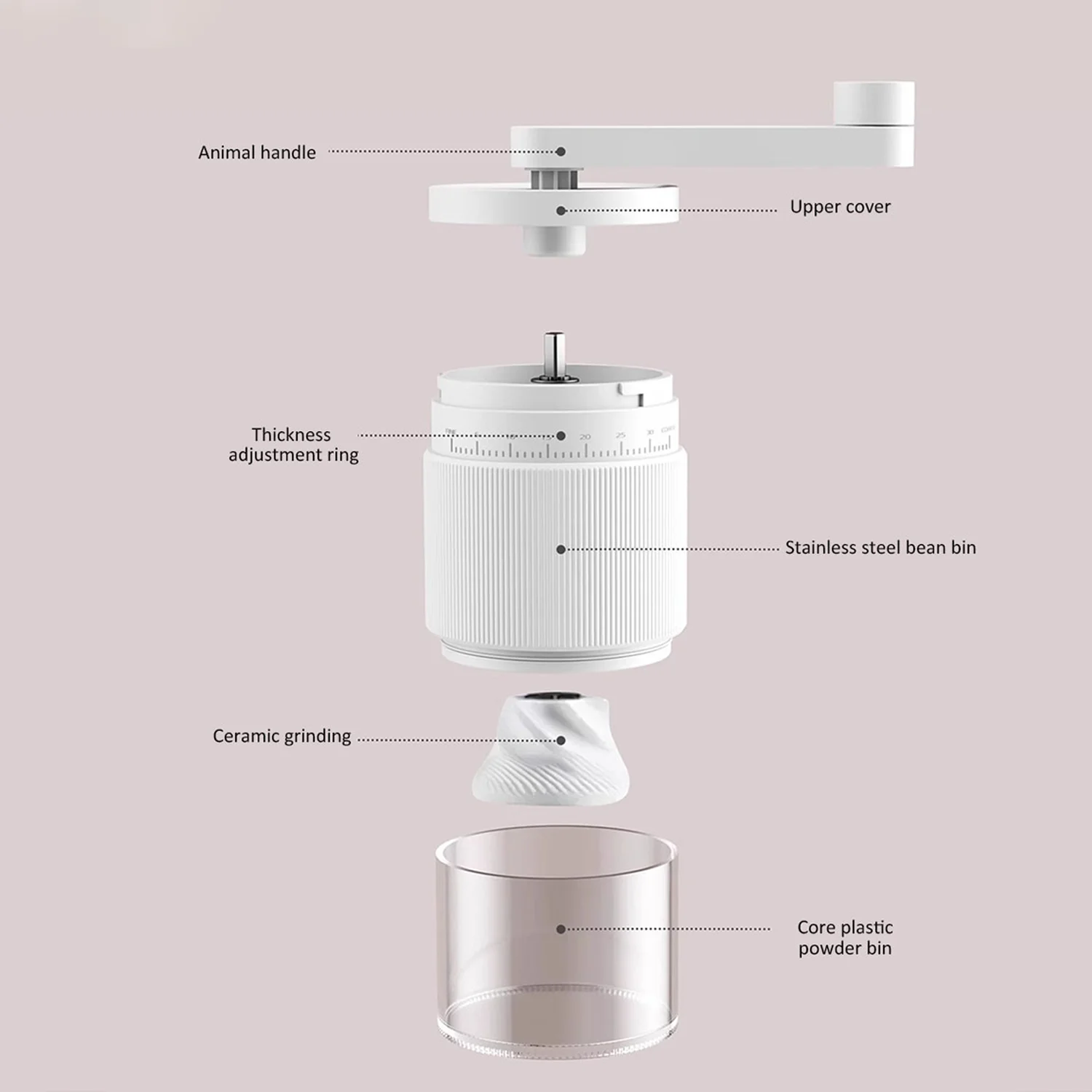

Advanced Burr Coatings and Treatments
Modern burr manufacturing goes beyond basic materials, with specialized coatings dramatically enhancing performance. These treatments represent the cutting edge of grinding technology.
| Coating Type | Base Material | Key Benefits | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | Steel | 3-5× longer lifespan, reduced friction, gold appearance | High-volume use |
| Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Steel | Extreme hardness, lowest friction, excellent heat resistance | Premium espresso grinding |
| Red Speed | Steel | Enhanced wear resistance, reduced static, distinctive red color | Commercial settings |
| TiAlN | Steel | Superior oxidation resistance, high-temperature stability | Fine espresso grinding |
| BCN (Boron Carbide Nitride) | Steel | Near-diamond hardness, exceptional durability | Professional settings |
These coatings significantly affect performance metrics. For example, TiN coating can reduce burr temperature by 20-30% during extended grinding sessions compared to uncoated burrs. This temperature difference can be critical for preserving delicate flavor compounds in coffee.
The ultimate guide to burr materials for espresso explores how these premium options particularly benefit espresso preparation, where precise particle distribution is essential for proper extraction.
Selecting the Right Coffee Burr Material
Choosing the ideal burr material depends on your specific needs and brewing style. Consider these key factors:
Brewing Method Requirements
- Espresso: Ceramic or coated steel burrs provide the fine, consistent grind necessary for proper extraction
- Pour-over/Drip: Either material works well, with steel often providing better consistency for medium grinds
- French Press: Steel burrs typically excel at producing consistent coarse grounds
Usage Volume Considerations
- Light home use (1-2 cups daily): Standard ceramic or steel both perform well
- Heavy home use (multiple grinds daily): Hardened steel or coated burrs offer better durability
- Commercial use: Premium coated steel burrs provide the best combination of performance and longevity
Understanding the ceramic vs steel burr longevity expectations helps make an informed decision based on your budget and usage patterns. Our manual coffee burr grinders collection includes options optimized for different user needs.

Understanding Burrs in Manufacturing
Shifting to the industrial context, “burrs” refer to unwanted material that remains attached to a workpiece after machining processes like drilling, milling, turning, or stamping. These manufacturing defects form when metal deforms rather than cleanly separating during cutting.
Common burr types include:
– Rollover burrs: Material folds over the edge of the workpiece
– Poisson burrs: Caused by material bulging at the sides due to compression
– Breakout burrs: Form when material breaks away unevenly at exits
– Cut-off burrs: Created when parts separate from stock material
Proper deburring is essential for:
– Component fit and function
– Safety (preventing sharp edges)
– Surface finish quality
– Preventing premature wear or failure
– Meeting engineering specifications
The hardness and ductility of the workpiece material directly influence both burr formation and the appropriate deburring tool material. Harder workpiece materials generally require harder, more durable deburring tools.
Tungsten Carbide Deburring Tools
Tungsten carbide represents the premium standard for deburring tools due to its exceptional hardness (typically 9+ on the Mohs scale) and wear resistance.
Key Advantages:
- Maintains sharp cutting edges far longer than steel alternatives
- Excellent heat resistance during high-speed deburring
- Superior performance on hardened metals, stainless steel, and tough alloys
- Precision cutting ability for fine detail work
Common Applications:
- CNC machined components requiring precise edge quality
- Aerospace and automotive parts made from hardened metals
- Production environments requiring long tool life
- Complex geometries where tool flexibility is limited
Tungsten Carbide Varieties:
- Single-cut carbide burrs: Feature teeth in one direction for smoother finishing
- Double-cut carbide burrs: Have teeth crossing in two directions for faster material removal
- Aluminum-cut carbide burrs: Specially designed with deeper flutes to prevent clogging on softer metals
While tungsten carbide tools cost 3-5 times more than HSS alternatives, their significantly longer lifespan and superior performance on difficult materials make them cost-effective for professional applications.
High-Speed Steel (HSS) Deburring Tools
High-speed steel offers an excellent balance of performance and value for many deburring applications. This versatile material contains various alloying elements (tungsten, molybdenum, chromium, vanadium) that enhance its properties.
Comparing HSS to Tungsten Carbide:
- More affordable (typically 20-30% the cost of carbide)
- Easier to resharpen when dull
- Less brittle—can withstand more impact
- Better for softer workpiece materials
- Shorter lifespan (approximately 1/3 to 1/5 of carbide)
HSS deburring tools excel when working with:
– Aluminum and aluminum alloys
– Brass and copper
– Mild steel
– Many plastics and composites
Heat treatment variations significantly affect HSS performance. For example, M2 HSS has different properties than M42 cobalt-enriched HSS, with the latter offering better heat resistance and edge retention for more demanding applications.
Hand Burr Grinder, Hand Crank Coffee Grinder, Manual Espresso Grinder, Portable Coffee Grinder
Price range: $262.72 through $300.22 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageManual Burr Mill, Manual Coffee Grinder Stainless Steel, Manual Coffee Mill Grinder, Mechanical Coffee Grinder
Price range: $127.26 through $130.32 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageHand Burr Grinder, Manual Coffee Grinder Stainless Steel, Precision Manual Grinder
Price range: $183.64 through $187.52 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageCeramic Burr Coffee Grinder, Hand Burr Grinder, Hand Crank Coffee Grinder, Manual Coffee Bean Grinder
Price range: $59.17 through $59.96 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Abrasive Deburring Materials
Abrasive deburring methods use particles of hard materials bonded to wheels, discs, brushes, or other tools to remove burrs through controlled surface abrasion.
Common Abrasive Materials:
Aluminum Oxide
– Most widely used general-purpose abrasive
– Excellent for ferrous metals (steel, iron)
– Good balance of cutting ability and durability
– Available in multiple grit sizes for different finish requirementsSilicon Carbide
– Sharper cutting action than aluminum oxide
– Better suited for non-ferrous metals (aluminum, brass)
– Also effective on hard, brittle materials like ceramics
– Wears faster than aluminum oxideCeramic Abrasives
– Premium option with self-sharpening properties
– Superior performance on hardened steels
– Excellent heat resistance
– Longer life than conventional abrasivesZirconia Alumina
– Extremely tough and durable
– Excellent for aggressive stock removal
– Particularly effective on stainless steel
The binding material that holds these abrasives also affects performance. Resin-bonded wheels provide flexibility, while vitrified bonds offer durability. Abrasive brushes with nylon filaments impregnated with abrasive grit can access complex geometries that solid tools cannot reach.
Ceramic and Specialized Deburring Tools
Beyond conventional materials, specialized deburring tools address specific challenges in modern manufacturing.
Ceramic Deburring Tools
- Ultra-hard cutting edges (9+ on Mohs scale)
- Exceptional heat resistance
- Chemical stability when working with reactive metals
- Ideal for precision work on hardened materials
Diamond-Coated Tools
- Ultimate hardness (10 on Mohs scale)
- Excellent for deburring hardened steels, ceramics, and composites
- Precision edge control for critical components
- Significantly higher cost offset by superior performance on difficult materials
Ceramic Fiber Brushes
- Flexible tools containing ceramic filaments
- Access complex geometries and internal features
- Self-sharpening characteristics
- Effective on both ferrous and non-ferrous materials
The disadvantages of poor burr removal extend beyond aesthetic concerns—unaddressed burrs can cause component failure, create safety hazards, and accelerate wear in precision assemblies.
Matching Deburring Materials to Workpieces
Selecting the appropriate deburring tool material requires understanding the workpiece properties. This matching approach optimizes both results and tool life.
| Workpiece Material | Recommended Deburring Tool | Alternative Option | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soft Aluminum | HSS, Aluminum-cut carbide | Silicon carbide abrasives | Avoid loading/clogging |
| Mild Steel | HSS, Tungsten carbide | Aluminum oxide abrasives | Balance cost vs. volume |
| Stainless Steel | Tungsten carbide, Ceramic | Zirconia alumina abrasives | Heat resistance critical |
| Hardened Steel | Ceramic, Diamond-coated | Ceramic abrasives | Hardness differential required |
| Titanium Alloys | Tungsten carbide (specific grade) | Ceramic fiber brushes | Prevent work hardening |
| Plastics | HSS, Fine abrasives | Specialized plastic-cutting tools | Avoid heat generation |
For optimal tool life with any material:
– Maintain appropriate cutting speeds
– Use proper cooling/lubrication when needed
– Select the correct tool geometry for the application
– Consider automated deburring for consistent results on high-volume production
Our manual burr mill collection demonstrates various approaches to burr design that can be applied to both coffee grinding and manufacturing contexts.

Burr Material Selection Factors: Final Considerations
When evaluating burr materials for either coffee grinding or deburring applications, several universal principles apply:
Performance vs. Cost Considerations:
- Initial investment must be balanced against expected lifespan
- Higher-quality materials typically deliver better consistency and results
- Volume of use significantly impacts the value equation of premium materials
- Maintenance requirements vary by material and affect long-term costs
Environmental Factors:
- Ceramic materials generally require less energy to produce than tungsten carbide
- Coated tools often have longer lifespans, reducing replacement frequency
- Material recyclability varies significantly between options
- Some specialized coatings contain rare elements with limited availability
The choice between ceramic vs. steel grinder burrs parallels industrial deburring material selection—both require matching material properties to specific applications. Similarly, the flat burr hand grinder design demonstrates how tool geometry works with material properties to achieve specific results.
Is There a “Best” Material? The Context-Driven Answer
After examining the various materials for both coffee grinding burrs and deburring tools, it becomes clear there is no single “best” material for all applications. The optimal choice always depends on specific requirements:
For coffee grinder burrs:
– Ceramic excels for fine grinding with minimal heat generation
– Steel provides durability and consistency across grind sizes
– Coated burrs offer premium performance for high-volume use
– The brewing method should guide material selection
For deburring tools:
– Tungsten carbide delivers precision and longevity for hard materials
– HSS provides excellent value for softer materials and general use
– Abrasives offer flexibility across various applications
– Specialized materials address unique challenges like hardened metals or complex geometries
The best material for coffee grinders ultimately depends on individual priorities—flavor development, durability, heat management, or value. Similarly, the best deburring tool material depends on workpiece properties, production volume, and quality requirements.
FAQs About Burr Materials
Do ceramic burrs really produce less heat than steel burrs?
Yes, ceramic materials conduct significantly less heat than metal. Tests show ceramic burrs typically remain 15-25°F cooler during extended grinding sessions, helping preserve volatile flavor compounds in coffee.
How long do different burr materials last?
With regular home use, ceramic burrs typically last 1,000-1,500 pounds of coffee before noticeable degradation, while steel burrs average 500-1,000 pounds. Premium coated burrs can extend this to 2,000+ pounds.
Can I use the same deburring tool on different metals?
While possible, it’s not ideal. Tools designed for specific materials perform better and last longer. For example, aluminum-specific carbide burrs have geometry designed to prevent clogging in soft metals.
Are diamond-coated tools worth the premium price?
For hardened steels, ceramics, and other extremely tough materials, yes. Diamond coating provides unmatched durability and cutting ability that makes the investment worthwhile for these challenging applications.
How can I tell what material my coffee grinder burrs are made from?
Ceramic burrs are typically white or light-colored with a smooth, glass-like appearance. Steel burrs have a metallic appearance and are magnetic. Our hand burr grinder collection includes detailed material specifications for each product.